The old way of sending money to someone.
Before the core banking system was implemented in banks, people used different methods to send their money.
A demand draft is one such instrument that allows people to transfer money in such a way that they don’t have to carry a large sum of money to different locations.
It works like this: you deposit money at the bank and advise the bank to enable withdrawal at a specific location.
In return, the bank gives you a token in the form of a paper instrument. The other branch of the bank will honour the instrument upon presentation.

We have also seen postal money orders too. A way of sending money through a post office.
To send money with the electronic money order (eMO) service, we deposit a certain amount of money at the post office counter in the name of the person you want to send it.
The post office issues the money order against the said payee, and the postman delivers the money to the payee at his residence.
A postal money order may take a few days to complete the whole transaction.
In this post, we will be exploring some of the basics of a demand draft and trying to understand it’s uses and benefits.
Let’s see a few more details about a demand draft.
What is a Demand Draft?
As per NI Act 1881, a demand draft is a negotiable instrument that the bank issues to the buyer, directing the other bank branch to pay a specific person or party on demand or on presentation.
In layman’s words, a person purchases the DD instrument with a specific amount of funds to get it transferred to other parties.
A demand draft is as good as real money, which is why banks do not issue bearer demand drafts. It should always be an order-demand draft.
This means that on presentation to your bank, only you get the funds. So, in the demand draft, there are certain things that are worth knowing.

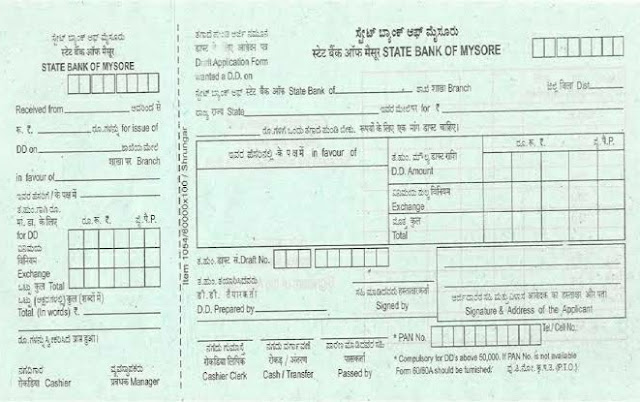
How to Purchase or Apply for a Demand Draft?
Purchasing a demand draft is easy. You can get it done within a few minutes.
Follow these steps to apply the same:
- Visit the bank where you want to get your demand draft.
- Get the demand draft application form from the counter.
- Fill it up, providing all the details such as the amount of the draft, payable to whom, payee branch, etc.
- Ask the demand draft issue charge and include it while filling out the form.
- Note that if the amount is less than ₹20,000, you can get it done by cash deposit; otherwise, it has to be purchased through an account or a cheque if the amount is beyond ₹20000.
- Submit the application form along with the funds to the designated counter.
- Wait for the printing of your demand draft.
- While handing it over to you, you have to make sure that the bank official has put the authorised signatory on the draft.
Some Useful Stuff
The purchaser cannot cancel the demand draft after delivering it to other parties for payment.
The demand draft is valid for 3 months.
The demand draft cannot be revalidated once it is expired or stale. It has to be cancelled and purchased as a fresh demand draft.
A duplicate demand draft can be obtained upon production of a letter of indemnity.
The original demand draft will not be paid if a duplicate demand draft is presented earlier and paid. It will be returned unpaid, stating that the duplicate demand draft is paid.
No demand draft can be issued in cash if the amount is more than ₹ 20000. It can be purchased only through the account payee, and a PAN number is mandatory to purchase it.
The Reserve Bank has made a PAN number mandatory to curtail money laundering under the Anti-Money Laundering Act, 2002.
Recently, RBI announced that it has been made mandatory to put the purchaser’s name on the demand draft.
Uses of Demand Draft
Once, demand drafts were a very popular mode of payment since it was much safer to carry demand drafts than carry a whole lot of money.
But as with everything good, it comes with its drawbacks. Money launderers took advantage of it and used it as a tool to defraud and launder money.
Moreover, during the manual time, it was very easy to forge at one point in time.
At present, it’s far safer than those old manual-demand drafts. Thanks to the new generation of technology that led to the end of the misuse of demand drafts.
The new version of this instrument is almost impossible to duplicate or forge.
There is no way it could hack and launder money, as the Reserve Bank has streamlined its issuance policy and put serious SOPs on it.
Some of the uses of demand drafts are as follows:
- Payment of school and college fees.
- Utility bill payment.
- Payment of any third party.
Earlier, all types of payments were common. It may even be sending money to anyone.
But the onset of the technology-driven mode of payment makes it worthless, as people nowadays prefer the instant payment model rather than the old-school, time-consuming money transfer.
The Online Payment Module
The trend of using demand drafts for financial transactions is getting obsolete. Nowadays, its uses are minimal.
Online payment modules, such as internet banking, card payments, and other third-party applications like Paytm, Google Pay, and Paypal, to name a few, have almost replaced all of the payments made using these instruments.
Certain institutes and government transactions are still relying on it. The rest are almost shifted to the instant payment type in CBS.
Difference between Demand Draft and Banker’s Cheque
The banker’s cheque and demand draft are just the same. Both of them are paper-based instruments governed under NI Act and both are negotiable instruments.
The only difference is that a banker’s cheque is for local payment.
It means this instrument is issued only for local payment, where a demand draft is issued for a specific amount ordered to be paid to a specific person on presentation anywhere. You can even purchase a foreign currency demand draft.
That means you can purchase a demand draft, ordering your banker to pay your friend who is staying in Delhi.
But here you need to transfer ownership of the demand draft to your friend, and on presentation of this demand draft by your friend to his banker, he would be able to withdraw the money, either by presenting it to the drawee bank or by collecting it through his banker for clearing.
Some terminology related to demand draft
| 1 | Drawer bank branch: Bank branch where a demand draft is issued. |
| 2 | Drawee bank branch: Bank branch where the demand draft is drawn. |
| 3 | Favour of: Where/Whom you intend to send the money. |
| 4 | Demand draft purchaser or drawer: The person who purchases the demand draft. |








What’s up, yes this paragraph is really good and I have learned lot
of things from it regarding blogging. thanks.
Feel free to surf to my web blog … More about the author